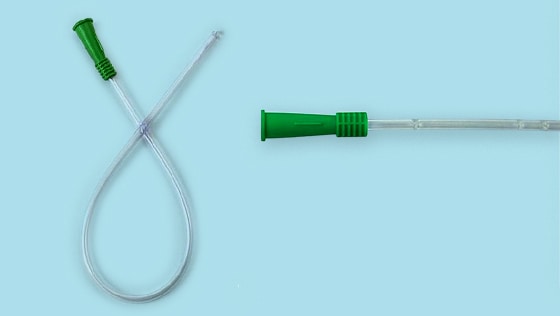
We have the right intermittent self-catheter for you.
Choose from a wide variety of intermittent self-catheters, plus FREE samples* from many suppliers.

Now Available
Patient Hub is a new way to manage your LMS account and place your reorders online! Get started with Patient Hub.

We can help find the best products for you
Our products and expertise can help you better manage your chronic conditions.
-
Urological Catheters
Check out our wide variety of catheter products or speak with a specialist about your needs. Browse catheters
-
Ostomy
Find the ostomy products and supplies that work best for you. Browse ostomy

Choose the correct urological catheter
Our most popular products
We have one of the largest inventories of quality medical supplies in the U.S.
Brava® Elastic Barrier Strips
Elastic — so they move with you. The Brava® Elastic Barrier Strip secures the position of the barrier and is elastic so it follows your body shape and movements. Brava® Elastic Barrier Strip is also available in other shapes to fit other body profiles and types of barriers.
MAGIC³ Go® Female Hydrophilic Catheter
The MAGIC³ Go® intermittent catheter is a hydrophilic, female length catheter with a robust handle for better control, a discreet consumer package and a new coating that maintains the catheter in a hydrated state so that it is ready to go out of the package.
Cure Catheter®
The sterile, single-use Cure Catheter® features polished eyelets on a straight or coudé tip with control stripe. It is offered in male, female, and pediatric lengths.
SpeediCath® Compact Plus
SpeediCath® Compact Plus offers the benefits of a ready-to-use hydrophilic-coated intermittent catheters in a small, discreet package.

Why Liberator Medical™ is liberating
Consider us an ally as we take the hassle out of your healthcare. We liberate you from lack of choice (with one of the largest inventories in the industry), and we can help you navigate insurance paperwork and prescriptions from healthcare providers.
-
We handle the headache of insurance and billing paperwork.
-
Our specialists will navigate your health plan benefits and answer any questions you may have.
-
Our dedicated specialists will contact your physician for you, making sure to get all the needed documentation.
-
We offer free (and discreet) shipping to your home or an alternate address.
Request more information
Tell us more about your needs and we’ll be in touch within 48 hours.
Customer testimonials
Don’t believe us. Our customers say it best.
Want free samples*?
Just fill out the form below, and we’ll be in touch. Or, call 1-855-948-3319 to speak with a product specialist.